The EA888 engine from the Volkswagen Group is famous for being supremely power-efficient, fuel-efficient, and reliable. And for decades, the engine has undergone successive revisions.
Gen 3 and Gen 4 are especially popular in daily drivers, including the Golf GTI and Audi A3. In this post, we’ll discuss some of the differences between these two generations and also some common issues that exist in the Gen 4 version.
สารบัญ
Differences between EA888 Gen 3 and Gen 4 engines
1. Cylinder head and exhaust design
2. Fuel injection system
3. Valve train and camshaft adjustment
4. เทอร์โบชาร์จเจอร์
5. ระบบทำความเย็น
6. Mild-hybrid integration
Common EA888 Gen 4 engine issues
1. Oil dilution
2. Mild-hybrid system issues (Gen 4 MHEV versions)
3. Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) issues
4. Turbocharger boost control problems
5. Crankcase breather valve issues
ความคิดสุดท้าย
Differences between EA888 Gen 3 and Gen 4 engines
1. Cylinder head and exhaust design

Gen 3
The EA888 Gen 3 offers an integrated exhaust manifold (IEM) built into the cylinder head. This innovation makes the exhaust gases travel a shorter distance, minimizing turbo lag and improving เทอร์โบชาร์จเจอร์ คำตอบ
It also helps the engine maintain its ideal operating temperatures by circulating exhaust gases through the engine coolant, making it run more efficiently. However, while effective, this design still left room for improvement in thermal efficiency and emissions management.
Gen 4
The Gen 4 goes one step further on the built-in ท่อร่วมไอเสีย, adding more cooling channels and a compact shape. This tuned arrangement lowers thermal inertia, allowing the engine to warm even faster and achieving better fuel economy at low-temperature starts.
It also integrates well with aftertreatment equipment (such as particulate filters and catalytic converters), which is crucial for compliance with stricter emission standards like Euro 6d and WLTP.
2. Fuel injection system
Gen 3
To help with the carbon build-up problems common with direct injection engines, the Gen 3 incorporated a dual-injection system consisting of direct injection (DI) and port fuel injection (PFI).
PFI cleans intake valves by spraying fuel through the ท่อร่วมไอดี, while DI ensures the right amount of fuel enters the combustion chamber. This system boosts the efficiency and longevity of combustion in a high-performance vehicle such as the Golf R.
Gen 4
The Gen 4 has a dual-injection system but tweaks the fuel delivery by adding high-pressure injectors that reach 350 bar (compared to ~200 bar on the Gen 3). This boosts fuel atomization, resulting in clean burning, responsive throttle, and more power. Moreover, they also minimize particulate emissions, which makes Gen 4 more environmentally friendly than Gen 3.
3. Valve train and camshaft adjustment
Gen 3
The Gen 3 features variable valve timing (VVT) in both the intake and exhaust เพลาลูกเบี้ยว. The engine regulates valve timing at engine load and speed, making the most of both air and combustion in an effort to maximize power and fuel consumption. However, the range of adjustment is somewhat limited compared to newer designs.
Gen 4
The cam phasing mechanism in the Gen 4 is much more refined and gives more customization options. This allows for greater fine-tuning of valve timing and better fuel economy at low RPMs and power at higher RPMs. This feature also aids in increased power delivery and throttle response.
4. เทอร์โบชาร์จเจอร์
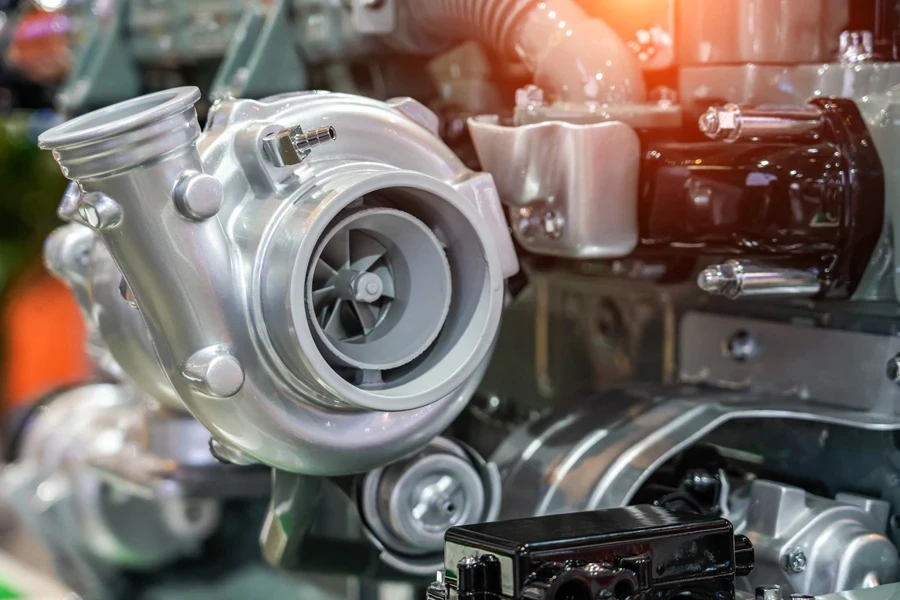
Gen 3
The Gen 3 engine uses a single-scroll turbocharger, providing plenty of low-end torque and peak power. However, single-scroll turbos are inefficient because exhaust pulses overlap, slowing down overall performance and turbo response in certain conditions.
Gen 4
Gen 4 switches to a twin-scroll turbo, which separates exhaust impulses from pairs of cylinders (i.e., 1-4 and 2-3). This arrangement helps with scavenging, so the turbo spins quicker and has less turbo lag. The result is a noticeable improvement in low-end torque and mid-range response that’s useful in day-to-day and performance driving.
5. ระบบทำความเย็น
Gen 3
The Gen 3 TSI engine has a standard cooling system where one เครื่องควบคุมความร้อน regulates engine temperature. Though promising, it wasn’t as precise as the modern systems at distributing heat between the cylinder block and head.
Gen 4
The Gen 4 features split-cooling technology, which allows independent cooling of the cylinder block and head. This enables the engine to reach operating temperature faster while maintaining optimal cooling during high-load conditions. The result is better thermal efficiency and reduced engine wear over time.
6. Mild-hybrid integration

Gen 3
The Gen 3 was not designed with electrification in mind, relying entirely on traditional combustion engine architecture. While efficient for its time, it lacks features like regenerative braking or coasting, which are common in modern engines.
Gen 4
The Gen 4 is designed to work with mild-hybrid systems featuring a 48-volt electrical architecture. This system enables features like start-stop, coasting mode, and regenerative braking, reducing fuel consumption and emissions.
For instance, when cruising, the engine can automatically shut off and use the mild-hybrid to power auxiliary devices.
อ่านเพิ่มเติม: Everything You Need To Know About EA888 Engines
Common EA888 Gen 4 engine issues
EA888 Gen 3 engine had some issues that rendered it, in some cases, unreliable. These include excess oil consumption, timing chain failure, thermostat issues, carbon build-up, and turbo problems.
With the development of the fourth generation EA888 engine, most of the issues with Gen 3 were resolved. Despite being more reliable, Gen 4 still has some issues. Here are some of the most common:
1. Oil dilution

Oil dilution, which occurs when unburned fuel mixes with engine oil, is one of the common issues with the Gen 4 EA888 engines. This can reduce the oil’s lubricating capabilities and may result in premature engine wear.
Oil dilution is more likely to happen in vehicles that are regularly driven a few miles or for long periods of time sitting idle, especially in cold weather. Modern emissions standards necessitate richer air-fuel mixtures during warm-up, increasing the likelihood of fuel entering the crankcase before complete vaporization.
Oil changes are important for preventing damage in the long run. By using premium synthetic oils, Volkswagen owners can keep their vehicles running smoothly. Moreover, letting the engine warm completely prior to driving it can help to reduce oil dilution risks.
2. Mild-hybrid system issues (Gen 4 MHEV versions)
เรื่อง Gen 4 EA888 engines have a 48-volt mild hybrid system that may occasionally fail due to sudden battery drainage, stalling, or malfunctioning.
Such problems are often caused by the hybrid system software not properly integrating with the engine ECU, resulting in communication failure or malfunction in the energy recovery system. Temperature extremes, like extreme hot or cold temperatures, can also strain the system and increase the likelihood of these problems.
These problems can be resolved through regular software updates at the dealership so that the system runs well. It may also be necessary to replace the problem if that is the root of the issues.
3. Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) issues
วาล์ว EGR and coolers are prone to clogging or failure, especially on cars intended for city use with stop-and-go traffic, short distances, and few highway miles.
A clogged EGR can result in many different conditions, from rough idling to power loss and emissions.
The most common reason for EGR problems is carbon build-up in exhaust gases, which can reduce EGR flow or corrode the valve and cooler.
This problem can be fixed by cleaning or swapping out the affected EGR components. In addition, preventive maintenance, like driving on the freeway every so often, can help eliminate carbon deposits, reducing clogging and increasing the life of the system.
4. Turbocharger boost control problems

Turbo boost control systems in the EA888 Gen 4 engines can experience issues such as inconsistent boost levels, delayed acceleration, or the vehicle going into “limp mode.”
Although less frequent than in earlier generations, these problems can still occur due to faulty electronic actuators or pressure sensors within the turbo system. Over time, these components may fail, disrupting boost pressure regulation.
Replacing the faulty actuator or re-adjusting the ECU should sort this problem out. It is also essential to replace the oil and air filter frequently in order to keep the turbo healthy and boost controls working properly.
5. Crankcase breather valve issues
The crankcase breather valve, an important part of the ระบบ PCV, can degrade, resulting in oil leaks, fires, or strange hissing from the engine compartment. A broken breather valve will also result in excessive oil use.
This usually is a result of a broken valve or deterioration in the material of the diaphragm, which will make the valve stuck open or closed, which interferes with crankcase pressure regulation.
The breather valve is typically a straightforward and inexpensive replacement. It’s also advisable to upgrade to PCV components made from more durable components to prevent the issue from recurring.
คุณอาจอ่าน: ปัญหาทั่วไป 7 ประการของเครื่องยนต์ Volkswagen EA888
ความคิดสุดท้าย
The EA888 Gen 3 and Gen 4 engines offer a balance of performance and reliability, with the Gen 4 featuring notable upgrades in turbocharging, fuel injection, and hybrid integration.
While both generations are strong performers, regular maintenance is crucial to prevent common issues like oil consumption, carbon buildup, and turbo failures.




